9 Challenges to Unlock Global Knowledge
Hard-to-find knowledge in documents is invaluable but difficult to extract, especially for complex languages like Arabic. Traditional search and generative AI both have significant limitations in accessing this information. RAG connects AI models to external knowledge sources, enabling more effective search and knowledge retrieval.
Unlocking Knowledge from Arabic Documents: Building Advanced RAG Systems
Starting with Arabic Documents
In today’s digital age, information drives progress and innovation. The vast expanse of hard-to-find knowledge—buried in documents—is invaluable to researchers, scholars, and professionals across various fields. From historical manuscripts to contemporary reports, these documents hold the potential to unlock new insights, foster cultural understanding, inform more effective decision-making, and lead to scientific breakthroughs.
Unfortunately, extracting and organizing such knowledge is fraught with challenges. Take Arabic documents for example: The unique complexities of the Arabic language, including its rich linguistic structure and script variations, present significant obstacles. Additionally, the scarcity of advanced tools and technologies tailored to the Arabic script compounds these difficulties, leaving much of this critical knowledge inaccessible. We’ve faced such challenges while working on AI-powered solutions that serve many languages and hundreds of millions of customers across the globe.
The Search Challenge in Arabic
Language-Specific Search Complexity
| Search Challenge | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Synonym Expansion | Arabic has 348 words for “lion” | Term expansion becomes prohibitive |
| Context Sensitivity | ”River bank” vs. financial “bank” | Meanings change in different contexts |
| Imprecise Queries | Looking for “1,931,512” but remembering “close to two million” | Exact term specification required |
| Fuzzy Memory | ”Books by a Chicago professor who visited Cairo in the middle of last century” | Complex, multi-faceted search criteria |
Moreover, finding information is challenging in any language: Modern search systems expand search terms to look for synonyms (e.g., “vehicle” when searching for “car”), which is prohibitive in a language like Arabic that has 348 words for “lion”. Expanding terms may get counterproductive as their meanings can change in different contexts (e.g., “river bank”). Searches may also fail or require many attempts because one couldn’t specify key terms correctly.
The Evolution of Search with Generative AI
For English and similar languages, modern search systems have evolved to use generative AI effectively to improve the search experience and go beyond finding needles in haystacks.
Generative AI Capabilities and Limitations
| Capability | Strength | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Conversation | Understands and responds in natural language | Confined to training data knowledge |
| Reasoning | Can analyze and synthesize information | Pattern recognition, not precise recall |
| Context Understanding | Grasps complex queries | Needs external knowledge for accuracy |
Generative AI models, on their own, are remarkably able to converse and reason in natural language; however, they are confined to knowledge in the source material used to develop them. In addition, said material helps teach these AI models patterns to recognize and follow (rather than precise recall of knowledge read).
Solution: To make effective use of language models in search, we connect them to external knowledge sources, similar to asking students questions in open-book exams. Techniques such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) blend the best of retrieval-based and generative AI techniques, enabling search systems to match knowledge to queries in more intuitive ways.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG finds indexed documents relevant to a search query then uses them as context for a generative large language model, such as Google’s Gemini, to synthesize responses. The results are grounded by the indexed corpus, richly informative, and contextually relevant.
RAG Benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Grounded Responses | Answers backed by actual documents |
| Rich Information | Comprehensive, synthesized insights |
| Contextual Relevance | Answers tailored to specific queries |
| On-the-fly Tasks | Extract, compare, tabulate information dynamically |
| Conversational | Natural dialogue instead of blue links |
Thanks to the reasoning and language understanding capabilities of such AI models, they can perform tasks on-the-fly (e.g., extracting information from multiple documents and tabulating a comparison) and can carry a conversation — no more pages of blue links. Adding RAG to conversational AI assistants greatly improves search experiences, offering more intuitive responses and addressing users’ needs more efficiently.
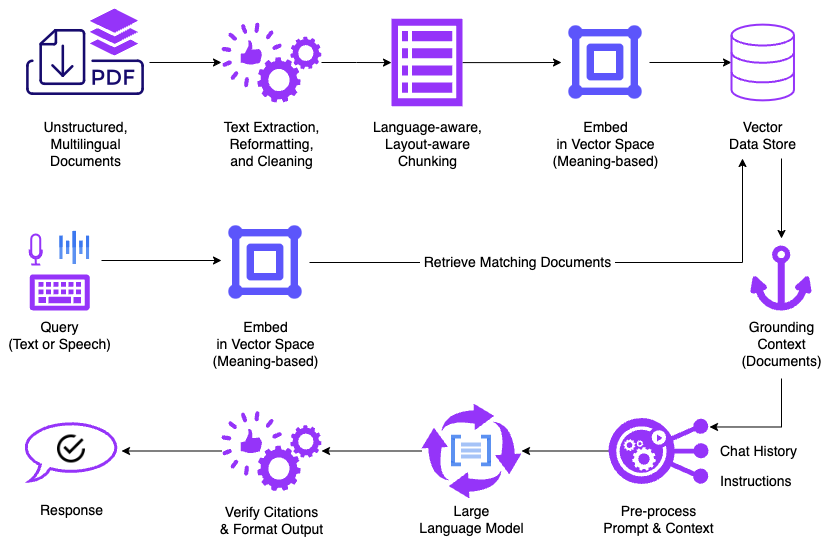
Retrieval Augmented Generation with a knowledge corpus of documents
The PDF Challenge: Why Arabic Text Extraction Is Hard
The diagram above shows a corpus of PDF files because they are the epitome of unstructured documents (as opposed to ones that strictly adhere to a known schema) and text content in PDFs—especially in Arabic—is notoriously hard for software tools to read.
Parsing Arabic text from PDF files presents several technical challenges, some of which are unique to the Arabic language and script, while others are common issues faced in parsing text from PDFs in general.
1. Complex Script Rendering
Character Shape Variations
| Position | Shape Example | Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Isolated | Different form | Extraction tools may misinterpret |
| Initial | Different form | Character shape changes |
| Medial | Different form | Contextual variations |
| Final | Different form | Position-dependent rendering |
Arabic is a complex script with characters that change shape depending on their position in a word (isolated, initial, medial, or final). This complexity can pose a challenge for text extraction tools, which may incorrectly interpret these variations.
Example of Extraction Errors:
وســجلت اقتصــادات دول أمريــكا الالتينيــة والكاريبــي تراجع ً ـا نسـبته 7.0 فـي المئـة فـي عـام 2020م
(Errors highlighted in red in original text)
2. Right-to-Left Writing Direction
Directional Challenges
| Aspect | Arabic | Most Languages | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Writing Direction | Right-to-Left (RTL) | Left-to-Right (LTR) | Text ordering issues |
| Tool Design | Rarely optimized | Primary focus | Alignment problems |
| Mixed Content | RTL + LTR numbers/English | Consistent direction | Complex parsing |
Arabic is written from right to left, which is opposite to many languages that are written from left to right. This can cause issues with text extraction tools that are primarily designed for left-to-right languages, leading to problems with text ordering and alignment.
3. Ligatures and Diacritics
Character Composition Complexity
| Element | Example | Storage Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Base Characters | ج ب ل ا | Individual glyphs |
| Diacritics | ِ ِ ّ ً | Separate markings |
| Combined Form | جِبِلًّا | Single visual unit |
| Ligatures | Multiple chars → one glyph | Not stored separately |
Arabic uses ligatures, where two or more characters are combined into a single glyph, and diacritics, which are small markings that change the pronunciation and meaning of words.
Example: “جِبِلًّا” is a combination of the following characters and markings: ج ِب ِل ّ ً ا
Challenge: Extracting these accurately can be challenging, as PDFs may not always store them as separate entities from their base characters; extracting such text from images in PDFs is even harder.
4. Encoding Issues
The way Arabic text is encoded in a PDF can vary; such variance can lead to Mojibake, the garbled text most of us have experienced when working with documents written in Arabic.
Encoding Problem Example
| State | Text Display |
|---|---|
| Corrupted (Mojibake) | الإعلان العالمى Ù„Øقوق الإنسان |
| Correctly Processed | الإعلان العالمي لحقوق الإنسان |
Our Solution: The text cleaning step in our ingestion pipeline takes care of messy data and files saved using mismatched encoding standards; the text above is ingested correctly.
5. Font Issues
Custom Font Challenges
| Issue | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Custom Fonts | PDFs use decorative, non-standard fonts | Incorrect character representation |
| Missing Fonts | Fonts not available to extraction tool | Missing text or crashes |
| Tatwil/Kashida | Text justification feature in Arabic | Confuses extraction tools |
| Missing Spaces | Combined with decorative elements | Lost word boundaries |
It’s very common for PDFs to use custom, decorative fonts. If the extraction tool doesn’t adapt to these, it can lead to incorrect character representations, missing text, or even crashes when loading the text.
Example combining missing spaces and Tatwil:
شـــهدت مؤشـــرات الأداء للأنشـــطة الاقتصاديـــةنموًاملحوظًاحيثتشـــيرالبيانات إلـــى أن النمـــو الأكبر كان في نشـــاط الصناعات التحويليـــة
Cost Impact of Decorative Characters
| Process Stage | Impact of Decorative Characters | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Indexing | Increased storage costs | One-time per document |
| Embedding | Higher processing costs | Less frequent |
| Retrieval | Slower matching | Per query |
| LLM Processing | Increased latency and cost | More frequent |
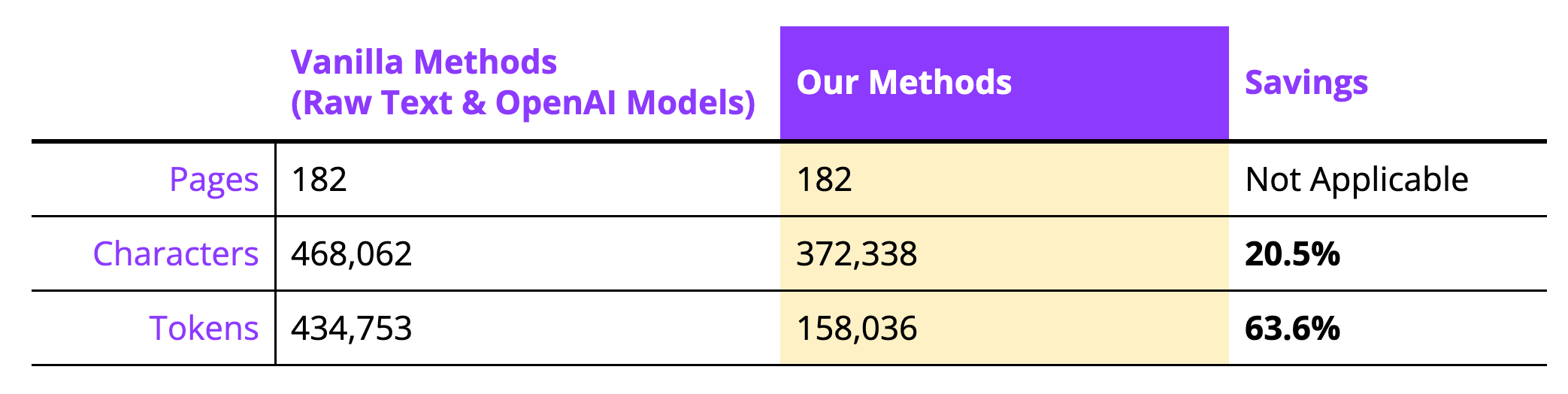
Moreover, decorative characters (such as Tatwil) increase the costs and latencies of storing, retrieving, and processing text — bloating search systems and hiking up bills. Recurring costs add up every time a document with decorative characters is indexed, passed to an embedding model, retrieved as a match for a query, passed to a large language model to process, and so on.
Our Solution: To reduce latency and cost, our RAG system cleans up text at ingestion, efficiently removing decorative characters while preserving meaning.
6. Non-Standard Text Layers
PDF Layer Complexity
| Layer Type | Content | Extraction Method |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Text | Searchable text layer | Direct extraction |
| Images | Text embedded in images | OCR required |
| Annotations | Comments, highlights | Specialized parsing |
| Forms | Form fields and data | Form-aware extraction |
PDFs can contain text in different layers, such as in images, annotations, or forms. Extracting text from these layers requires additional processing; Optical Character Recognition (OCR) might be needed for text within images.
Monta AI vs. ChatGPT Plus: OCR Capabilities
| System | OCR Support | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Monta AI | ✅ Advanced OCR | Successfully extracts text from images |
| ChatGPT Plus | ❌ Limited | Fails on image-embedded text |
Monta AI utilizes OCR when ingesting such elements:
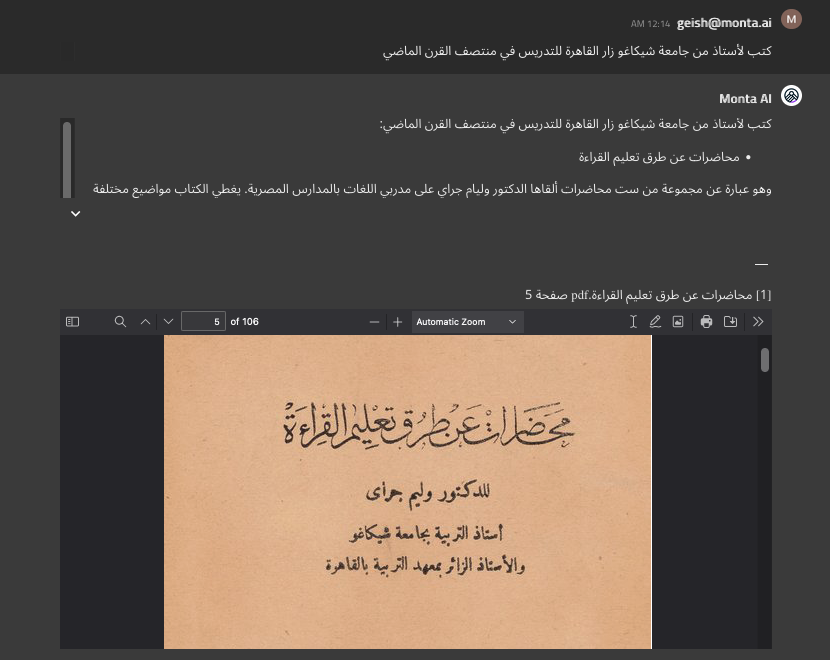
ChatGPT Plus, despite its astounding capabilities, failed to answer the same question (due to the need for OCR):
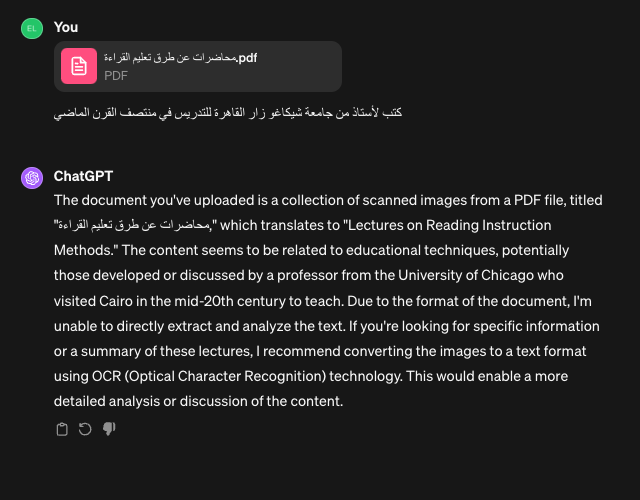
7. Formatting and Layout Issues
PDFs often use complex layouts and formatting, which can include tables, columns, forms, footnotes, and embedded images. Understanding the intended structure of the document when parsing it can be a difficult task, especially when the layout is non-linear or interrupted.
Complex Layout Challenges
| Layout Element | Challenge | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Tables | Multi-cell data extraction | Financial reports, statistics |
| Multi-column | Reading order determination | Newspapers, academic papers |
| Forms | Field identification and extraction | Applications, surveys |
| Footnotes | Reference linking | Research documents |
| Embedded Images | Context understanding | Mixed-media reports |
Example: Complex Table Extraction
(Highlights in screenshots below were added to help readers of this blogpost find relevant information in the referenced PDFs)
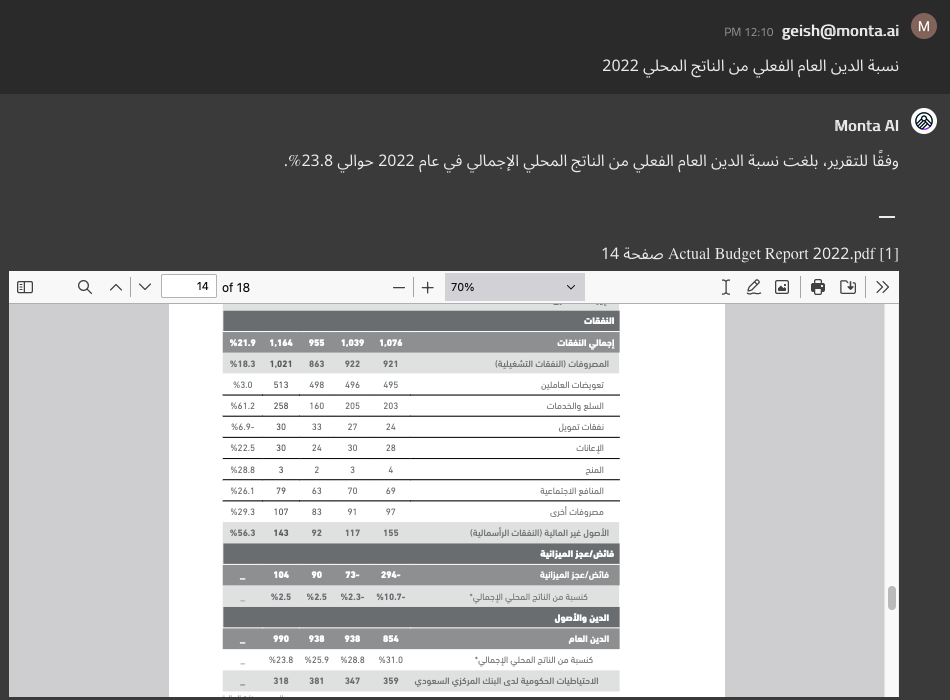
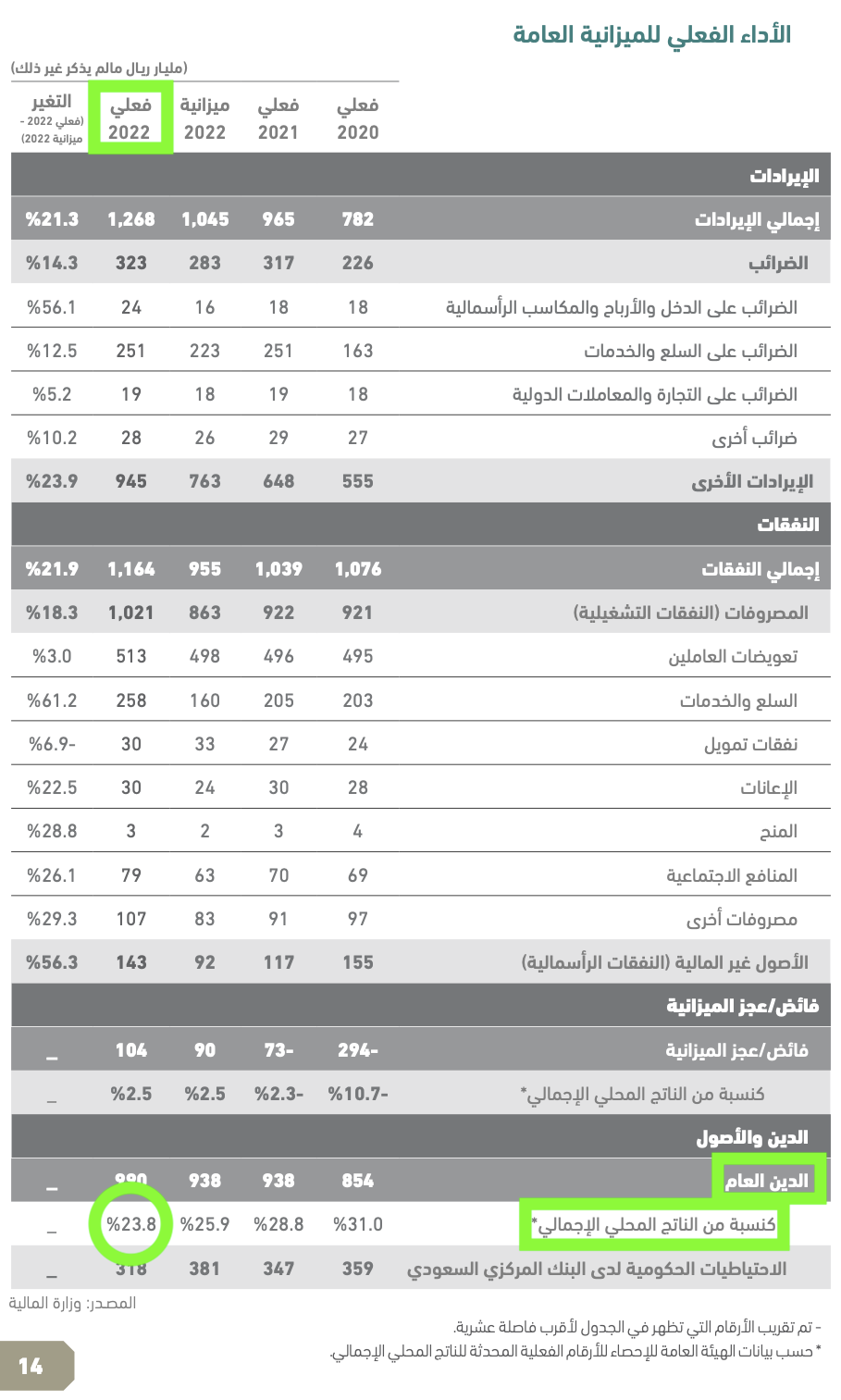
Layout-Aware Processing Capabilities
Multi-page, Multi-column Flow:
Layout-aware ingestion enables Monta AI to answer questions when the text is flowing from one column to another and across multiple pages while interrupted by a table — all at the same time:
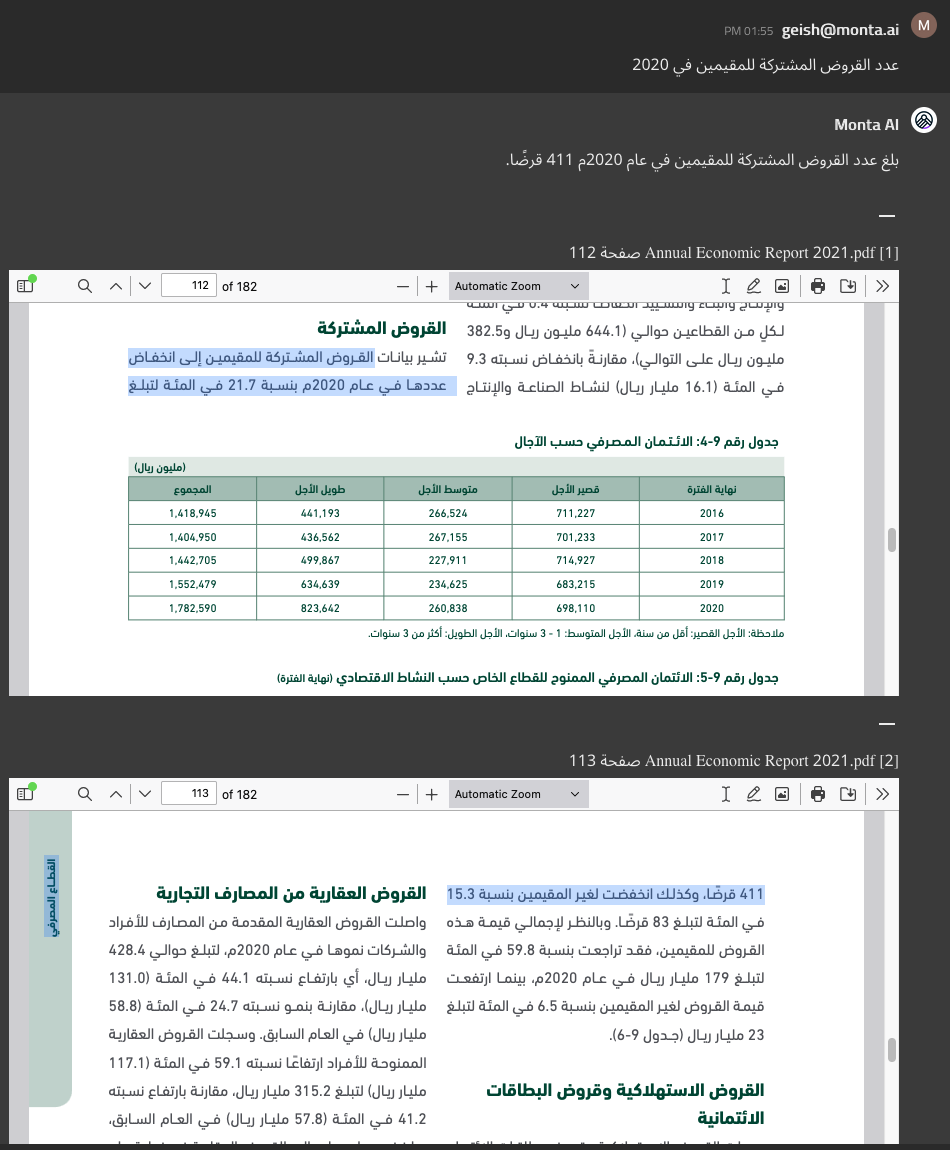
Comparison: Monta AI vs. ChatGPT Plus
| Feature | Monta AI | ChatGPT Plus |
|---|---|---|
| Layout Understanding | ✅ Advanced | ❌ Limited |
| Multi-column Flow | ✅ Accurate | ❌ Fails |
| Form Extraction | ✅ Precise | ❌ Cannot determine |
Layout understanding matters, as shown by the lacking answer ChatGPT Plus gave for the same query:

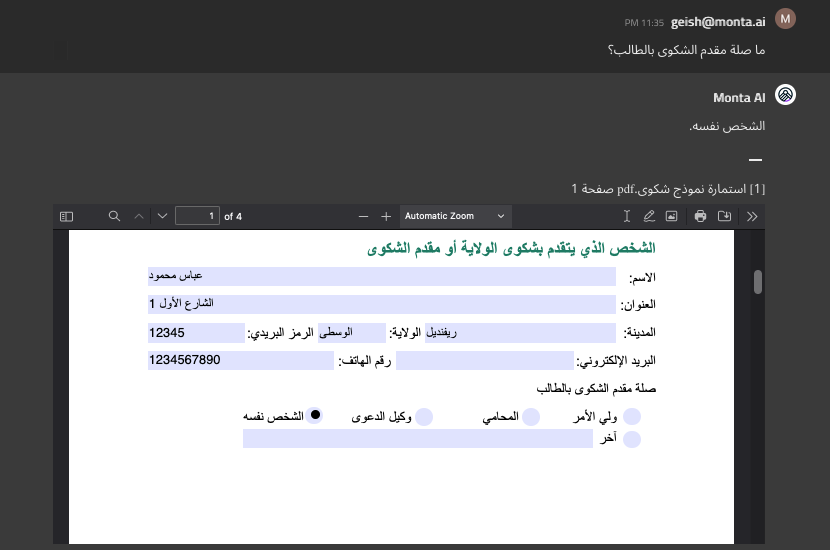
Form Control Understanding
Monta AI’s assistant correctly answers questions about information (e.g., a radio-button selection) in a form thanks to understanding form controls and the custom reformatting steps in ingestion:
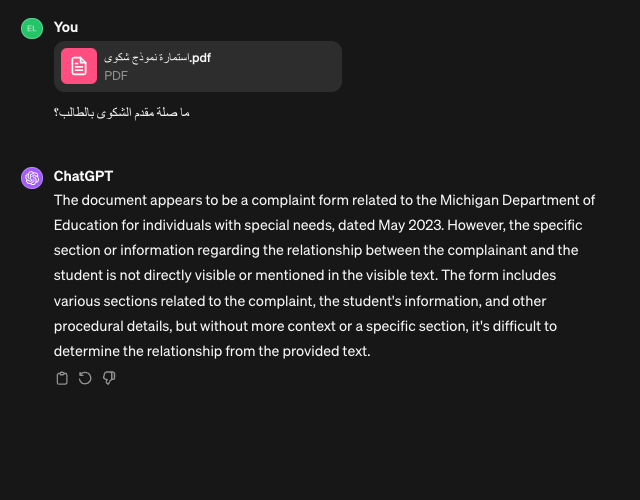
When asked the same question, ChatGPT Plus gave a verbose—yet dissatisfying—explanation as to why it couldn’t determine the answer:
8. Chunking
To ingest a knowledge base of PDFs in preparation for enabling search, they need to be broken down to smaller pieces in a process known as chunking.
Chunking Strategy Challenges
| Approach | Chunk Size | Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Too Small | Individual sentences | Context gets lost, atomic units break |
| Too Large | Multiple paragraphs | Context diluted with irrelevant info |
| Simplistic (period-based) | Variable | Abbreviations confused as sentence ends |
| Optimal (Monta AI) | Semantic boundaries | Preserves meaning and context |
The Challenge: Determining chunk boundaries effectively is a challenging task: make them too small and context gets lost as atomic units break into multiple chunks; make them too big and context gets diluted with irrelevant, confusing information.
Why Simple Methods Fail:
| Method | Problem |
|---|---|
| Sentence splitting | Periods in abbreviations confused as end-of-sentence |
| Fixed character count | Breaks mid-thought or mid-word |
| Paragraph-based | Paragraphs may be too long or too short |
Our Solution: To understand the flow and boundaries of atomic units conducive to effective search, our RAG system takes cues from the meanings of various textual and non-textual elements in a PDF (language-aware and layout-aware).
9. Generative-AI Issues
To generate answers given relevant evidence and citations, a large language model (LLM) is used to understand and generate Arabic text.
LLM Performance Trade-offs
| Aspect | Challenge | Our Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Arabic Understanding | Most LLMs weaker in Arabic | Specialized Arabic-optimized models |
| Processing Cost | Capable LLMs are expensive | Efficient model selection |
| Response Time | Quality models take longer | Performance optimization |
| Output Format | Often too verbose | Context-aware formatting |
Capable LLMs take more time and cost more to produce high-quality responses. As mentioned earlier, our RAG system uses AI models that are better at understanding Arabic and do so more efficiently, speeding up processing time and saving costs.
Intelligent Output Formatting
| Query Type | Optimal Format | Traditional LLM Output |
|---|---|---|
| Comparison | Table | Wall of text |
| Multiple items | Bullet list | Long paragraphs |
| Simple fact | Inline citation + PDF page | Verbose explanation |
Moreover, LLMs tend to be too verbose and produce walls of text to answer questions that are better answered as a table, a list, or a short commentary on an inline PDF page that has the answer, all of which are formats our RAG system automatically understands and produces based on the query and given context.
Monta AI’s Comprehensive Solution
Technical Capabilities Summary
| Challenge Area | Monta AI Solution | Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Script Rendering | Shape-aware character recognition | Handles all positional variants |
| RTL Processing | Bidirectional text handling | Correct ordering and alignment |
| Ligatures & Diacritics | Advanced character composition | Accurate extraction |
| Encoding | Robust normalization pipeline | Handles Mojibake and mismatches |
| Font Issues | Adaptive font handling + Tatwil removal | Cost-efficient processing |
| OCR | Advanced image text extraction | Surpasses ChatGPT Plus |
| Layout | Multi-column, table, form-aware | Complex document understanding |
| Chunking | Semantic boundary detection | Optimal context preservation |
| Arabic LLMs | Specialized Arabic models | Faster, cheaper, more accurate |
To effectively parse PDFs, Monta AI combines an ensemble of specialized techniques developed to handle the complexities of the Arabic script and language, as well as the general challenges of extracting text from PDFs.
Our Differentiators:
- 🔍 Beyond Text Extraction - Understand content using layout and metadata cues
- 🎯 Intelligent Context Selection - Choose relevant information for responses
- 📄 Source Citation - Display embedded pages used to formulate answers
- 💡 Format Optimization - Automatic selection of tables, lists, or prose based on query
- ⚡ Cost Efficiency - Reduced latency and processing costs
- 🌐 Arabic Expertise - Purpose-built for Arabic script complexities
Our systems go beyond extracting text to understand the content of PDFs using cues such as layout and metadata, aiding the entire solution to provide highly accurate answers in an intuitive format. The AI assistant decides which relevant context to use to respond to queries, while citing and displaying embedded pages used to formulate the response.
Conclusion
The journey to unlock the vast reservoirs of knowledge contained within Arabic documents is fraught with unique challenges, ranging from the linguistic intricacies of the Arabic language to the technical hurdles of parsing text from PDFs. Yet, the advent of technologies like multilingual RAG-powered AI assistants heralds a new era of possibilities.
The Path Forward
| From | To |
|---|---|
| Inaccessible Knowledge | Unlocked insights from Arabic documents |
| Technical Obstacles | Seamless extraction and processing |
| Limited Understanding | Deep cultural and linguistic comprehension |
| Isolated Information | Connected, searchable knowledge bases |
By combining multilingual embedding models and LLMs with specialized techniques for dealing with complex scripts and document formats, we are on the cusp of making this wealth of information easily accessible to a global audience.
As we continue to refine these technologies and methods, the promise of seamlessly extracting and leveraging the rich insights hidden in Arabic documents becomes much closer to a tangible reality, lighting the way for future innovations and discoveries for all languages around the globe.